- Home
- Our Chapter
- Our Profession
- Certification (CHES)
What is CHES?
The CHES (pronounced chez) designation signifies the individual has met eligibility requirements for, and has successfully passed a competency-based examination demonstrating skill and knowledge about the Eight Areas of Responsibilities for Health Educators, upon which the credentials are based.
How does one obtain skills in and knowledge of the Areas of Responsibility?
The foundation for obtaining experience in the Areas of Responsibility is academic training. Many professional preparation programs in health education or related degree programs at colleges and universities have designed their curricula using the Eight Areas of Responsibility for Health Educators. Eligibility for the CHES examination is based solely on possession of a degree and/or academic preparation related to health education.
What are the Areas of Responsibility?
There are Eight Areas of Responsibility for Health Education Specialists that make up the standards of the CHES/MCHES credentials. They are:
- Area I: Assessment of Needs and Capacity
- Area II: Planning
- Area III: Implementation
- Area IV: Evaluation and Research
- Area V: Advocacy
- Area VI: Communication
- Area VII: Leadership and Management
- Area VIII: Ethics and Professionalism
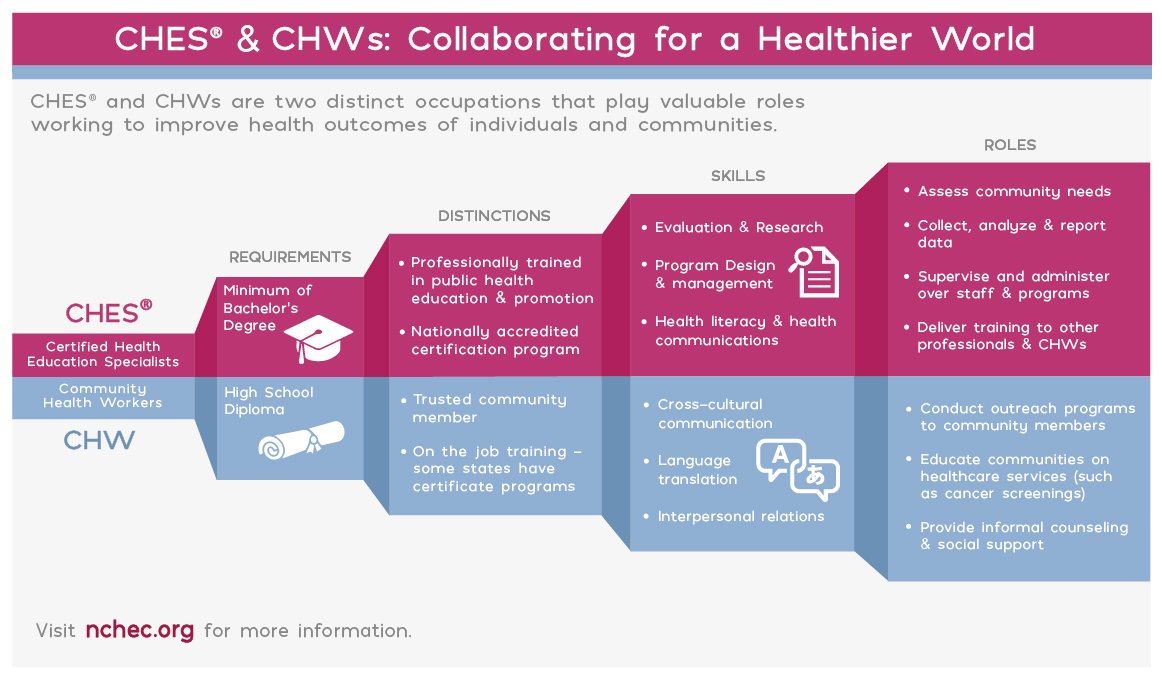
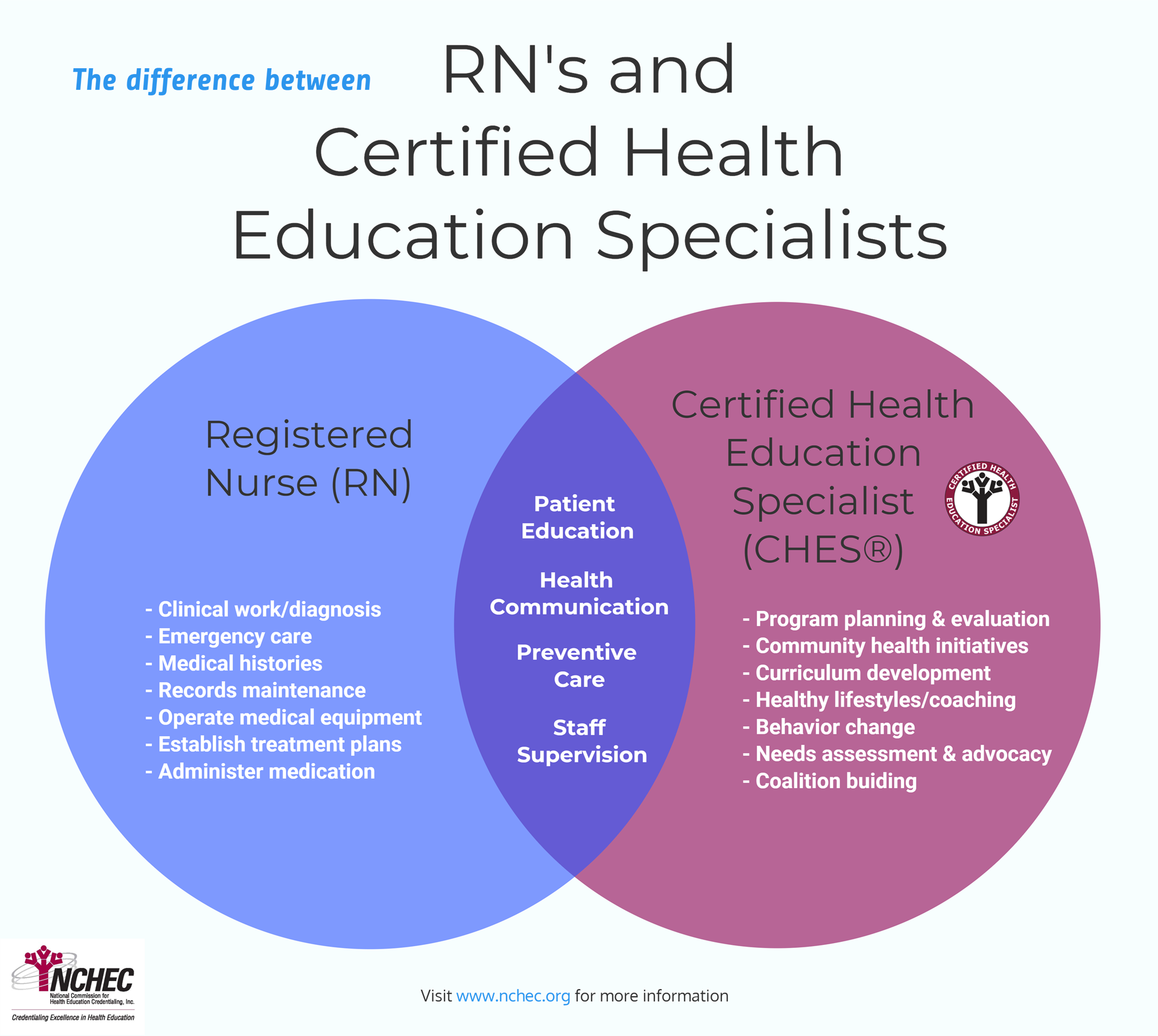
What is a Health Education Specialist?
Health education specialists are professionals who design, conduct and evaluate activities that help improve the health of all people. These activities can take place in a variety of settings that include schools, communities, health care facilities, businesses, universities and government agencies.
Health education specialists are employed under a range of job titles such as patient educators, health education teachers, health coaches, community organizers, public health educators, and health program managers.
What is a Certified Health Education Specialist?
Certified Health Education Specialists (CHES) are those who have met the standards of competence established by the National Commission for Health Education Credentialing Inc. (NCHEC) and have successfully passed the CHES examination. Eligibility to take the CHES examination is based exclusively on academic qualifications. An individual is eligible to take the examination if he/she has:
A bachelor's, master's or doctoral degree from an accredited institution of higher education; AND one of the following:
- An official transcript (including course titles) that clearly shows a major in health education, e.g., Health Education, Community Health Education, Public Health Education, School Health Education, etc. Degree/major must explicitly be in a discipline of "Health Education." OR
- An official transcript that reflects at least 25 semester hours or 37 quarter hours of course work (with a grade "C" or better) with specific preparation addressing the Eight Areas of Responsibility and Competency for Health Educators
What does the CHES designation mean?
The CHES designation after a health educator's name is one indication of professional competency and commitment to continued professional development.
What does the MCHES designation mean?
The MCHES designation after a health education specialist's name is one indication of professional advanced-level compentency and commitment to continued advanced-level professional development.
What are my responsibilities after certification?
The certification period for CHES is five years. During that time a CHES must accumulate 75 hours of continuing education. Each year the certification is renewed with an annual fee of $70. On the fifth year, the CHES recertifies by demonstrating completion of 75 continuing education contact hours (CECH) and paying the annual fee.
The MCHES continuing education requirements are similar to the CHES, as an individual will need 75 credits in five years to recertify. The 75 CECH required for recertification must include at least 45 hours of Category I CECH (NCHEC approved opportunities) and no more than 30 hours of Category II CECH (events that meet NCHEC standards but are not offered by a Designated Provider). MCHES are required to earn 30 CECH that are directly related to the advanced-level Sub-competencies from Category I and/or II for each certification cycle. For more information on the continuing education requirements view the Policies and Procedures Handbook.
For more information go to the web page for the National Commission for Health Education Credentialing, Inc. (NCHEC), http://www.nchec.org, or see the attachment below, "Building a Better Team: The Business Case for NCHEC Certification"


|